Original Research
Management Control System, Environment Uncertainty and Managers’ Performance: Organization Commitment as a Moderating Variable
- Abstract
- Full text
- Metrics
This study uses organizational commitment as a moderating variable to examine how management control systems and environmental uncertainty affect manager performance. Thirty-four respondents were selected from among the organizations at Perum Bulog South Sumatra and Bangka Belitung Representative Office that are involved in the management control system at upper to middle management levels. A questionnaire was used to collect data. Multiple regression analysis and moderated multiple regression analysis were used for the testing. The results revealed that management control system positively and significantly impacted manager performance, but manager performance was unaffected by environmental unpredictability. The impact of environmental unpredictability and the management control system on managers' performance cannot be mitigated by organizational commitment at Perum Bulog of South Sumatra and Bangka Belitung Representative Office.
|
Management Control System, Environment Uncertainty and Managers’ Performance: Organization Commitment as a Moderating Variable |
|
|
Accounting Department, Faculty of Economics, Universitas Sriwijaya Palembang, Indonesia |
|
|
KEYWORDS |
ABSTRACT |
|
Management Control System, Environment Uncertainty, Managers’ Performance, Organizational Commitment |
This study uses organizational commitment as a moderating variable to examine how management control systems and environmental uncertainty affect manager performance. Thirty-four respondents were selected from among the organizations at Perum Bulog South Sumatra and Bangka Belitung Representative Office that are involved in the management control system at upper to middle management levels. A questionnaire was used to collect data. Multiple regression analysis and moderated multiple regression analysis were used for the testing. The results revealed that management control system positively and significantly impacted manager performance, but manager performance was unaffected by environmental unpredictability. The impact of environmental unpredictability and the management control system on managers' performance cannot be mitigated by organizational commitment at Perum Bulog of South Sumatra and Bangka Belitung Representative Office. |
|
Correspondence: |
|
Introduction
Information technology advancements recently had an impact on corporate operations. Global business competition is getting more and more intense. To meet this requirement and raise the value of the company, managers must be able to put sound business concepts into practice. This is being done in order to help the business succeed in the fiercely competitive business world. Globalization, technological advancements, the growing use of new technology, and the creation and application of knowledge are only a few variables influencing this competition (Heliani, 2019). Similar to what occurs in Indonesia, all companies operating inside the country's economy must contend with fierce worldwide competition in order to remain in business. A State-Owned Enterprise (SOE) is one of these commercial enterprises. One of the economic players with a purpose, SOE is presently dealing with the difficulties of escalating international competitiveness in the business sector.
It is anticipated that SOE will be able to boost productivity in order to develop into a robust corporate entity. It also has an obligation to consider its relationships with other entities and facets of national life. An SOE is a state-owned organization whose primary goal is to assist in the growth of the state and national economies. It is also mandated to turn a profit, though this is not its primary goal. Professional management of SOE is necessary in all domains, including control, supervision, implementation, and planning. In order to accomplish corporate objectives, management must constantly work to develop and refine business strategy. The degree of performance attainment attained by managers is indicative of successful management.
Manager performance (MP) is really less stable in SOE due to a phenomenon. The profits the business has made demonstrate this. Performance-related issues are plaguing a number of SOEs; specifically, the business is losing money. 2011 saw multiple instances of state losses caused by SOE, which was another issue with SOE. The state lost a total of IDR 92.93 billion in 13 instances as a result of management's carelessness, which included inadequate project management and control as well as disregard for the work plan and budget of the organization (Heliani, 2019). The Indonesian Ombudsman drew attention to Perum Bulog's rice stock storage strategy in 2021. Perum Bulog is a company involved in food logistics. Too much time is spent storing rice inventories in warehouses, which could impair the quality. Inadequate operational and financial oversight led to this case (Fatika, 2022). This example demonstrates that for any business to work at its best, planning and control are essential for keeping things running smoothly and in line with the objectives of the organization. A management control system (MCS) is one instrument for managing this. A strong MCS can boost output and help the business reach its objectives (Heliani, 2019).
MCS seeks to guide and guarantee that the strategy put into practice is in line with the objectives of the company. The features of the company in question have a significant impact on how MCS is implemented there. In addition, MCS seeks to inspire the accomplishment of both task and strategic initiatives. An organization can help and coordinate its decision-making process by implementing MCS as a data collection tool. Planning and control systems (MCS) are tools that managers can use to develop and implement strategies (Sari & Saragih, 2020).
MCS falls into the applied behavioral science category. In essence, this system expects us to manage and oversee a business that is deemed successful based on specific presumptions (Kosbiantor, et al, 2018). The complexity of management control varies depending on the size of the organization; the more sophisticated the control system, the larger the firm scale. MCS is made up of procedures and structures. The responsibility centers are the main focus of the management control structure. A work unit headed by an individual accountable for the responsibilities entrusted to them is known as a responsibility center. The informal exchange of information and interactions between managers and staff is the main emphasis of the management control process. Informal communication can be expressed through facial expressions, meetings, dialogues, and memos. In addition to informal control, businesses also employ formal control procedures, such as interconnected stages for reporting, budgeting, programming, measuring, and evaluation (Anthony & Govindarahan, 2011).
Diverse developments occur in the organizational setting when the external environment is dynamic, for example, when government regulations change. Under these circumstances, managers encounter difficulties forecasting the external environment, making planning and control procedures more challenging and fraught with issues (Einhorn et al., 2023). Delegating authority and offering a broad range of information can help managers who are experiencing difficulties with environmental uncertainty (EU) in planning and control operations (Sani & Andriany, 2020). Organizations may need to make changes to their environment and organizational settings as a result of EU. If people believe the environment is unpredictable and are unable to forecast how environmental components will change, they will have high EU.
Organizational commitment (OC) and managers' effective performance in line with organizational goals are inextricably linked. In this instance, OC is devoted to helping all implementers and managers carry out organizational tasks by taking part in budget preparation and accounting control systems in order to meet the required manager performance. Strong OC will motivate lower-level managers to work really hard to meet established organizational objectives. Additionally, OC can inspire innovative ideas from employees to help managers perform their jobs better (Hartini & Lestari, 2018).
Prior studies have largely concentrated on managers' performance in private businesses. The variables in this SOE research have not been used in many other investigations. MCS evolved in SOEs; members of the EU and OC are not the same as those in private enterprises. As a result, variables used in private organizations to evaluate the value of manager performance are employed by researchers interested in researching SOE. The chosen SOE is a business that manages and schedules significant national needs, particularly for Bangka Belitung and South Sumatra regions.
Literature review and hypothesis development
Applied Behavior Science (ABS)
ABS is a guideline regarding methods of running and controlling a company that is considered good based on certain assumptions (Kosbiantoro, et al, 2018). ABS aims to comprehend, forecast, and alter human behavior in the actual world—particularly within businesses. Enhancing individual and group outcomes is the main objective of ABS, which focuses on researching and evaluating human behavior in certain circumstances. ABS develops treatments, strategies, and policies that can improve behavior, enhance decision-making, and enhance the well-being of individuals, organizations, and communities at large through the use of empirical research methods and evidence-based practice.
ABS serves as a manual for putting behavioral scientific disciplines' insights and concepts to use in understanding, predicting, and influencing behavior in everyday situations. The ultimate objective is to create methods and treatments that lead to behavioral change to improve individual and group outcomes (productivity, well-being, and satisfaction). ABS aims to create treatments that can promote positive behavioral changes by thoroughly grasping behavioral drivers, such as beliefs, social norms, and environmental factors. This field provides individuals, companies, and communities with effective tools and methods to overcome obstacles and accomplish goals by fusing scientific knowledge with real-world applications.
ABS is employed in studies to clarify how MCS, EU, and OC influence MP. Companies utilize the MCS model to manage every aspect of the business in order to accomplish shared objectives. This applied behavioral understanding includes MCS as a system made up of different subsystems. A good organization needs to be able to accomplish a number of goals. In essence, the elements of any business are the same and are called WERE (Work, Employee, Relationship, Environment). EU is a requirement that affects how business management behaves in order to accomplish targeted outcomes (Einhorn et al., 2023). There is a shared commitment within the firm that supports the successful attainment of these shared goals.
Management control system (MCS)
MCS is a series of actions and activities that occur in all organizational activities and run continuously (Sumarsan, 2013). MCS is a crucial component of the overall system that management uses to plan and coordinate business operations. The elements of MCS comprise two parts: (1) management control structure, which includes organizational structure, responsibility center, delegation of authority, performance measurement, and information and communication systems; and (2) management control process, which includes budget preparation, implementation, evaluation, and strategic planning (Guspinda et al., 2021). The goals of MCS are to (a) encourage managers to put in a lot of work to accomplish top management goals; (b) give managers the right incentives to make decisions that align with top management goals; (c) Equitably assess the rewards managers receive in relation to their abilities and efforts, as well as the quality of their decision-making (Arjalies et al., 2013; Blocher et al., 2001).
To put ideas into action and accomplish corporate goals, businesses require a management control system. MCS is a system created to handle environmental unpredictability to compete with rivals. It is anticipated that efficient MCS will boost business performance. The business environment, technology, organizational structure, organizational scale, organizational strategy, and organizational culture are some of the internal and external aspects that might affect MCS design (Chenhall, 2003).
EU is one of those unpredictable external factors. EU can be understood as managers' lack of knowledge about the external environment to comprehend or forecast the future (Bateman & Snell, 2007). EU is the lack of knowledge that is pertinent to a decision, and decisions made during their various roles can determine whether a decision is successful or unsuccessful (Mardiana & Handayani, 2018). This indicates that because there is insufficient information available, it is challenging for businesses to decide whether the choice is correct. According to other academics, EU is an activity taken when an individual lacks sufficient knowledge to predict future circumstances (Wati & Damayanti, 2017). This indicates that a person cannot forecast future events because the information required is either unavailable or insufficient. As a result, a person cannot forecast future events.
EU denotes environmental factors outside the company's control that may impact its operational choices and decisions. This may occur as a result of incomplete information provided to the organization when discussing a matter. People feel uneasy because they believe they do not know enough to make reliable predictions (Kartika, 2010). When making future predictions, a person's ability to make sense of external information plays a significant role. Hence, EU is the lack of confidence in pertinent external sources of information that affect each and every choice made by an individual or organization. All information pertaining to the decisions taken is relevant information in this context. EU is also strongly correlated with future prediction accuracy. A person's ability to predict future events increases with decreasing EU. Conversely, the higher the EU, the harder it is for someone to forecast the future.
Organizational commitment (OC)
OC is the degree to which each member of the organization aspires to continuously contribute to the organization and uphold its status within it (Suhardi, 2020). Workers take these actions because they support the organization's objectives. OC was defined by Sutanto and Ratna (2015) as a person's relative strength toward a specific organization, which is characterized by three psychological factors: (1) a strong desire to stick with a particular organization, (2) a desire to put in the maximum amount of effort for the organization, and (3) a firm belief in and acceptance of the organization's principles and objectives.
Three types of organizational commitment (OC) have been identified by Allen and Meyer (1993). Affective commitment is the first type, which relates to workers' emotional connection, identity, and involvement in the company. In this scenario, employees remain in an organization for personal reasons; (2) continuation commitment relates to the things that employees must give up if they wish to quit the organization. In this instance, workers choose to remain with an organization because they believe it to be a means of meeting their needs, or, to put it another way, workers as individuals depend on the organization; (3) normative commitment, which refers to workers' views of the obligations of the organization. Workers stick with a company because they feel obligated to show loyalty to it. Employees do this action because they understand how important it is to show dedication to the company. Workers with a strong sense of commitment and loyalty to the firm will be very motivated to see it succeed. Employee commitment increased as their awareness and involvement in the organization grew. According to Manetje & Martins (2009), a disgruntled employee or one who is not committed to the company will seem to be leaving through turnover or absenteeism.
OC is a mutually trusting attitude that can take many different forms, including loyalty and a desire to stick around. The degree of loyalty exhibited by employees is contingent upon both the individual and the organization. Employees who work for companies that share their values will be motivated to strive for the company's development. This results from employees' perception that when they grow the business, they are also growing themselves. OC encompasses not just the aspiration to stay a member of an organization but also to accomplish objectives in tandem with the organization.
Performance is the accomplishment of a goal. Nursam (2017) explained that performance is the degree of task completion success and the capacity to meet predefined objectives. The performance might be considered good and successful if the intended aims are successfully attained. MP can be understood as the manager's contribution to organizational activity. MP reviews differ according to the company culture they have created.
According to Jusuf (2013), MP indicators consist of eight dimensions: (1) Planning, which includes the capacity to establish objectives, guidelines, and actions/implementation, as well as work scheduling, budgeting, procedure design, and programming; (2) The capacity to gather and communicate data for records, reports, and accounts, as well as for monitoring outcomes, figuring out inventory, and job analysis, Evaluation refers to the capacity to appraise and quantify proposals, observed or reported performance, employee, financial report, outcomes record, and product inspection assessments; (4) Coordination, or the capacity to communicate with individuals in different areas of the company in order to link and modify programs, alert other departments, and establish connections with other managers; (5) Supervision, which includes managing subordinates, giving work assignments, guiding, training, and explaining work regulations to subordinates, and leading leaders; (6) Staff management, which includes hiring, interviewing, and choosing new hires, placing, promoting, and transferring staff members; (7) Negotiation: This refers to the capacity to engage in sales, purchases, or contracts for goods and services; it also includes liaising with suppliers, haggling with sales representatives, and group bargaining; (8) Representative: This involves attending business association meetings, attending meetings with other companies, giving speeches at community events, engaging in community outreach, and advocating for the company's overarching goals.
Theoretical framework
This study employs multiple linear analyses as a framework to investigate the effects of MCS and EU on MP, as well as the role of OC as a moderating variable in the interaction between MCS and EU on MP. Testing of this moderating variable was done to find out whether OC would increase or decrease the impact of MCS and EU on MP. The reasoning behind this study has been illustrated in the figure 1.
Theoretical Framework
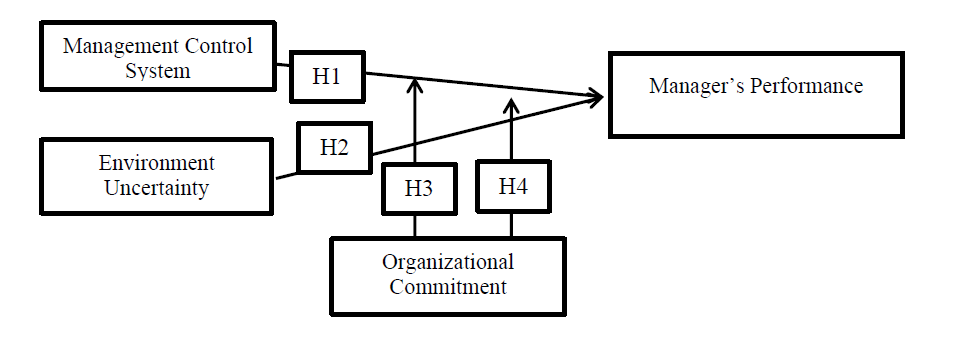
Hypothesis development
The effect of management control systems on manager’s performance
Applied behavioral science theory categorizes MSC as part of the theory itself. This theory states that, basically, an MCS contains demands on us regarding how to run and control a company that is considered good based on certain assumptions. Each company has a different complexity in MCS; the larger the company scale, the more complex it will be (Kosbiantoro, et al, 2018). MCS can be applied to all companies under various conditions. MCS can be applied to several companies with almost the same characteristics and business scale. Junita et al. (2018) stated that implementing a MCS is one way to achieve good company financial performance. The goal of MCS is to provide information that helps with decision-making, planning, control, and evaluation. MCS plays a very important role in managing the company's internal control. Research by Nursyamsir et al. (2023), Sandanafu et al. (2017), Ilias et al. (2016), and Durendez et al. (2016), prove that MCS influences company performance. This shows that the better MCS is implemented, the better the company's performance. The first hypothesis can be formulated as follows:
H1: There is an influence of the management control system on manager performance.
The effect of environmental uncertainty on manager performance
The applied behavioral science theory explains that a company that is considered well must be able to fulfill several components, one of which is the environment. EU perceived by the business as arising due to the company's uncertain external conditions must be addressed by company management so that it can produce effective management decisions in dealing with the EU perceived by the business (Eriani & Fanani, 2019). Managers are more motivated to interact with all the potential that the company has so they can overcome problems that arise due to the EU perceived by the business to meet organizational expectations. Research by Adhikara et al. (2022), Ilmy (2021), Aprisma and Sudaryati (2020), Kwiotkowska and Gebczynska (2018) and Mukherji and Mukherji (2017) proves that EU influences MP. Based on the explanation, the hypothesis that can be built is
H2: Environmental uncertainty influences manager performance.
Organizational commitment can moderate the relationship between management control systems and manager performance.
In the theory of applied behavior science, MCS is categorized as part of this theory. MCS contains demands regarding how to run and control a company that is considered good (Kosbiantoro, et al, 2018). Each company has a different complexity in MCS; the larger the company scale, the more complex it will be. Strong OC within an individual will cause the individual to try hard to achieve organizational goals in accordance with the goals and interests of the organization and will have a positive outlook and strive to do the best for the interests of the organization (Wiratno et al., 2016). High commitment makes individuals prioritize the organization rather than personal interests and try to make the organization better. Managers tend to act in their personal interests if organizational commitment is low. OC can be used as a psychological tool in running an organization to achieve expected performance. Evan et al. (2020) found that OC can moderate the relationship between self-efficacy and employee performance. Based on the statement above, the hypothesis can be built:
H3: Organizational commitment can moderate the influence of management control system on manager performance.
Organizational commitment can moderate the relationship between environmental uncertainty and manager performance.
Testing of the influence of the EU on MP has been carried out and inconsistent conclusions have been produced. To overcome this, the author takes an ABS theoretical approach, which explains that basically every company has the same components, namely Work, Labor, Relationships and Environment. Every human behavior is influenced by the surrounding environment. However, accepting the influence of the environment depends on each personality type. This means that everything that happens to an individual with this personality type assumes that he is the cause of everything that happens in his life. A person with high commitment will not easily leave the organization where he works; this affects turnover in the organization. High commitment makes employees even more motivated to work actively. This enthusiasm for work can positively influence the company because they consider the company to be themselves, which concerns the livelihood of all parts of the company (Hutama & Susilowati, 2021). Huseno (2017) found that OC influences EU. Based on the explanation above, the hypothesis that can be built is H4: Organizational commitment is able to moderate the relationship between environmental uncertainty and manager performance.
Method
Population and sample
Population is a generalization area consisting of objects/subjects that have certain qualities and characteristics determined by researchers to be studied and then conclusions drawn (Sugiyono, 2019). In this research, the population consists of individuals directly involved in MCS or managers at the manager level at Perum Bulog South Sumatera Representative Officeel, totaling 35 people. 1 regional leader, 1 deputy regional leader, 5 branch heads, 4 managers, and 24 assistant managers. This research uses a saturated sample, namely, the entire population is sampled.
Analysis techniques
The data in this research will be analyzed using the SPSS (Statistical Pages for Social Sciences) version 25 application. Previously, hypothesis testing was carried out, and validity, reliability, and classical assumptions were first tested.
Multiple linear regressions are an equation that describes the relationship between more than one independent variable and one dependent variable (Rinaldi et al., 2021). This means this equation contains two or more independent variables and only one dependent variable. Multiple linear analysis models to test the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. The equation in this regression is:
MP = α + β1MCS + β2EU + β3OC + e …………………………………………………. (1)
Moderated Regression Analysis was carried out to see the influence of moderating variables in a research model. Moderating variables appear to find out whether these variables are able to strengthen or weaken the relationship between the dependent and independent variables. The moderation regression model is:
MP = α + β1MCS + β2EU + β3OC + β4MCS*OC + β5EU + e ………………………… (2)
Measures
Management control system
MCS is a system that must be designed so that the actions of each company employee to achieve their interests can also help the company's goals (Amalia, et al, 2021).
Environmental uncertainty
EU is a situation where there is a lack of appropriate information needed to make a decision. This EU can be measured using a questionnaire (Kartika, 2010).
Moderating variables
Moderating variables are variables that weaken or strengthen the influence of the independent variable on the dependent variable (Solimun et al., 2017). The moderating variable in this research is OC. OC has a strong desire to remain a member of an organization. This commitment is demonstrated by the continuous loyalty of workers to the organization for the success and welfare of the organization (Gunawan & Santioso, 2015). All variables were measured using a 1-5 interval Likert scale where 1 represents strongly disagree and 7 represents strongly agree. Table 1 shows the definition of the variables and their indicators.
Table 1.
Variable definition and measurement
|
variable |
definition |
indicators |
item no |
|
Management Control System |
A system that must be designed so that the actions of each company employee to achieve their interests can also help the company's goals (Amalia, et al, 2021) |
Organizational structure |
1 |
|
Delegation of Authority |
2 |
||
|
Responsibility Center |
3 |
||
|
Performance Measurement |
5 |
||
|
Information and Communication Systems |
6 |
||
|
Strategic Planning |
4 |
||
|
Budget Preparation |
7 |
||
|
Implementation |
8 |
||
|
Evaluation |
9 |
||
|
Environmental Uncertainty |
A situation where there is a lack of information needed to make decisions (Kartika, 2010) |
Availability of information sources |
10, 11 |
|
Confidence in doing work |
12, 13, 14, 15, 16 |
||
|
Confidence in the decisions taken |
17, 18, 19 |
||
|
Ignorance of external factors that can influence decision-making |
20, 21 |
||
|
Organizational Commitment |
A strong desire to remain a member of an organization (Gunawan & Santioso, 2015) |
Affective Commitment |
22, 23, 24 |
|
Continuity Commitment |
25, 26 |
||
|
Normative Commitment |
27, 28, 29 |
||
|
Manager’s Performance |
Management's ability to carry out management functions which are business activities, which of course always relate to decision-making (Animah et al., 2021) |
Planning |
30 |
|
Investigation |
31 |
||
|
Coordination |
33 |
||
|
Evaluation |
32 |
||
|
Supervision |
34 |
||
|
Staffing |
35 |
||
|
Negotiation |
36 |
||
|
Representative |
37, 38 |
Results and discuss
General description of research objects
The questionnaires were distributed at the Perum Bulog Organization, South Sumatra, and Babel Representative Offices. Distribution of the questionnaire was carried out by distributing the questionnaire link online. This was done because the target respondents were not only in the Palembang area but also spread across districts/cities in South Sumatra and Bangka Belitung. The questionnaires will be distributed and collected from March 14, 2023, to March 25, 2023. The following are details of the questionnaire distribution. Of the 35 target respondents, only 34 questionnaires were successfully taken and filled out completely and 1 questionnaire could not be processed because it was empty. Thus, 34 questionnaires can be processed.
General description of research respondents based on gender and length of service, are shown in Figure 2.
Profile of participants 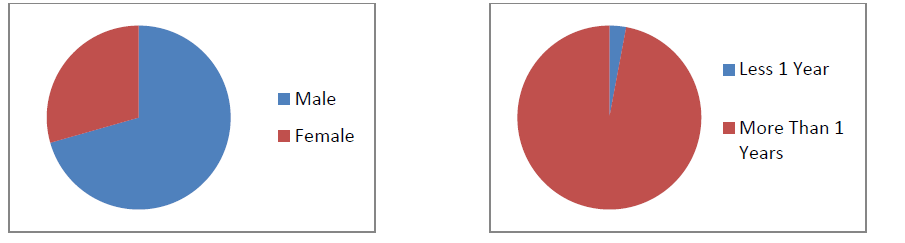 Based on gender, of the 34 respondents, 24 (71%) were male and 10 (29%) were female. Meanwhile, based on the length of time a person has served in a particular position, from the 34 respondents, one person (3%) has held that position for less than one year, and 33 other people (97%) have held the position for more than one year.
Based on gender, of the 34 respondents, 24 (71%) were male and 10 (29%) were female. Meanwhile, based on the length of time a person has served in a particular position, from the 34 respondents, one person (3%) has held that position for less than one year, and 33 other people (97%) have held the position for more than one year.
Testing data result
The results of research data testing can be seen in the Table 2.
Test results table
|
|
Β |
t |
Significant |
|
Without Moderating |
|
|
|
|
Constant |
6.855 |
0.940 |
0.354 |
|
MCS |
0.508 |
2.394 |
0.023* |
|
EU |
0.231 |
1.539 |
0.134 |
|
With Moderating |
|
|
|
|
Model 1 |
|
|
|
|
Constant |
1.573 |
0.211 |
0.834 |
|
MCS |
0.483 |
2.375 |
0.024* |
|
EU |
0.134 |
0.883 |
0.384 |
|
OC |
0.332 |
1.996 |
0.055** |
|
Model 2 |
|
|
|
|
Constant |
14.892 |
0.214 |
0.832 |
|
MCS |
-0.696 |
-0.300 |
0.767 |
|
EU |
0.905 |
0.878 |
0.387 |
|
OC |
-0.031 |
-0.014 |
0.989 |
|
MSC*OC |
0.035 |
0.508 |
0.616 |
|
EU*OC |
-0.023 |
-0.757 |
0.456 |
|
Adjusted R Square |
0.361 |
||
|
Dependent Variable is MP; *significant 0.05; **significant 0.10 |
|||
Sources: Data Processing, 2023
From the results of the multiple regression tests, the following equation can be created:
MP = 1.573 + 0.483MCS + 0.134EU + 0.333OC + e
1) The constant value is 1.573. This means that if the independent variables (MCS, EU, and OC) are zero, then MP is worth 1.573 percent.
2) MCS coefficient value is 0.483. This means that if the value of MCS increases by one unit, MP increases by 0.483, assuming that the other variables remain constant.
3) EU coefficient value is 0.134. This means that if the EU increases by one unit, MP increases by 0.134, assuming the other variables remain constant.
4) OC coefficient value is 0.333. This means that if OC increases by one unit, MP increases by 0.333, assuming the other variables remain constant.
Moderated regression analysis
Moderated Regression Analysis was carried out to see the influence of moderating variables in a research model. Moderating variables appear to find out whether these variables are able to strengthen or weaken the relationship between the dependent and independent variables. The results of the moderated regression are as follows;
MP = 14,892 - 0,696MCS + 0,905EU - 0,031OC + 0,035MCS*OC - 0,023EU*OC + έ
1) Constant value is 14.89. It means that if all independent and moderating variables are zero, then the MP value is 14,892 percent.
2) MCS coefficient value is -0.696. This means that if the MCS value increases by one unit, the MP value decreases by 0.696, assuming that other variables remain constant.
3) EU coefficient value is 0.905. This means that if the EU value increases by one unit, the MP value increases by 0.905, assuming that other variables remain constant.
4) OC coefficient value is -0.031. It means that if the OC value increases by one unit, the MP value decrease by 0.031, assuming the other variables remain constant.
5) The coefficient value of the first moderating variable (the interaction of MCS with OC) is 0.035. This means that when the value of this variable increases by one unit, the MP value increases by 0.035, assuming the other variables remain constant.
6) The coefficient value of the second moderating variable (the interaction of EU with OC) is -0.023. This means that when the value of this variable increases by one unit, the MP value decreases by -0.023, assuming the other variables remain constant.
Coefficient of determination (R2)
The Determination Coefficient (R2) is used to determine the percentage of independent variables that together can explain the dependent variable. The coefficient of determination value is between zero and one. If the coefficient of determination (R2) = 1, it means that the independent variable provides the information needed to predict the dependent variables. If the coefficient of determination (R2) = 0, it means that the independent variable is unable to explain its effect on the dependent variable. The test results show that the regression model built with the MCS, EU, and OC variables is only able to explain MP by 36%. Meanwhile, the remaining 64% is explained by other variables not examined in this study.
The testing result found that MCS has an influence on MP is proved with a value of significant 0.023 < 0.05, then the first hypothesis in this study is accepted. Meanwhile EU has no effect on MP, as proven by the value sig. 0.134 > 0.05. Thus, the second hypotheses are rejected.
The type of moderation of OC on this regression model is a moderator homologiser because β3 (the coefficient of regression of OC) is insignificant, and β4 (the interaction of OC and MCS) is also insignificant. Thus the third hypothesis was rejected.
When regressed to MP, the second moderation variable (interaction between EU and OC) also refers to an insignificant influence proven with a significant value of 0.456 > 0.05. This means that OC is unable to moderate the relationship between the EU and MP. Thus, the fourth hypothesis is rejected. The type of moderation of the OC in this regression is a moderator homologiser because β3 (the coefficient of regression of OC) is insignificant, and β5 (the interaction of OC and EU) is also insignificant.
The impact of the management control system on the performance of managers
The H1 test found that MCS has a positive impact the MP of Perum Bulog Sumsel and Babel Representative Office. Based on the strategic planning information obtained, it can be said that Perum Bulog of the Sumsel and Babel Representative Office have implemented the MCS well. It is seen from the regular and periodic budgeting programming is the implementation of the strategy implemented by the company, and performance evaluation is also done by comparing the budget implementation with the budget given. Besides, information grouped by program has been used as a basis for the future.
An MCS is a tool for monitoring and observing the implementation of management control that tries to direct the organization's goals in the company so that the performance performed by the management of the company can run more efficiently and smoothly. The applied behavior science theory also states that the MCS applied by an organization leads to various ways in which the desired goals can be achieved through the performance of the manager. Then, the better the MCS, the higher the MP, the greater the involvement of the top middle managers; the middle down the manager will be better (Badollahi et al., 2022).
These results are in line with Nursyamsir et al. (2023), Wahyuni and Lestari (2019), Ilias et al. (2016) and Durendez et al. (2016). This means that an MCS plays a very important role in the company. Failure to implement an MCS has an impact on the company. Therefore, the better MCS companies give assurances to the company to be able to achieve the company's primary goal of improvement of performance.
The impact of environmental uncertainty on the performance of managers
The test results showed that the EU did not affect the MP of Perum Bulog Managers in the Sumsel and Babel Representative Office. Then, H2 was rejected. These results show that the EU is unable to explain the variation in the performance effectiveness of managers. This study shows that increased environmental inequality makes it difficult for managers to plan and control. Planning and control is problematic if it is not possible to predict what will happen in the future. It can be understood that the higher the EU, the lower of MP.
These results are inconsistent with those of Hayati and Yulistia (2023) and Kwiotkowska and Geczynska (2018). With the high level of uncertainty, companies tend to use non-financial information in larger proportions and more effectively in addressing the EU. This is also supported by the theory of ABS, which states that the environment as a whole can be viewed as a source of information and as a stock of sources of information as well as as as stock of resources (Cushing & Kusasih, 2017). EU leads to a major deviation between what was planned and what was realized. This leads to uncertainty over performance.
Organizational commitment can moderate the relationship between management control systems and manager performance
The H3 test found that OC was able to moderate the relationship between MCS and MP of Perum Bulog manager’s in the Sumsel and Babel Representative Office. OC in this equation is homologiser moderation variables that do not interact with independent variables and have no significant relationship with dependent variables. H3 is thus rejected.
This can happen because even if a manager has a high level of OC because of the pressure from superiors and the competition from colleagues, the manager becomes difficult to express his affection for the organization, and OC cannot moderate the relationship between MCS and MP. This means that managers in the company are improving MCS not because they have a high OC but because the organizational structure forces them to participate or because it is just a task.
This finding is inconsistent with the ABS theory raised in this study, where the theory is part of MCS. This theory says that there are components in the company that make the organization run well, namely the relationship and the employee (Arilaha & Seber, 2019). OC is a characteristic of the relationship of the member of the organization with its organization. A good manager is a manager who places the interests of the company above the interests of the individual, prioritizing the organization's interests, which implies an improvement in the manager's performance.
These results also contradict Leiwakabessy (2021) who proves that OC moderates the relationship between MCS and MP. High OC will facilitate the organization to implement adequate management controls so that it can give adequate confidence to stakeholders that the organization has achieved managerial performance effectively and efficiently.
Organizational commitment can moderate the relationship between environmental uncertainty and manager performance.
The H4 test found that OC was able to moderate the relationship between EU and MP of Perum Bulog Managers in the Sumsel and Babel Representative Office. OC on this regression model acted as a moderation of homologiser that did not interact with independent variables and did not have a significant relationship with dependent variables. Thus the H4 in this study was rejected. These results show that the high OC of managers is not a problem in favor of an increase or decrease in managers' performance due to EU. There is a high OC that does not always give good results for the MP in Perum Bulog in the Sumsel and Babel Representative Office.
This study contradicts the theory of ABS, which states that environmental components must be met in order to be a good company. A manager may feel uncertain about what action to take in the face of the dynamics of suppliers, competitors, customers, and consumers, or the possibility of relevant environmental changes such as technological, cultural, demographic, etc. (Suparmun, 2015). Under such conditions, in order to maximum performance, management requires an OC to reduce the level of uncertainty. Achieving the organization's goals becomes important for individuals/employees with high OC. With a clear perception of the goal, the manager will have a commitment, which can motivate each manager to the goal and goal.
The results of this study contradicted Anwar (2018), who found that when moderated by OC, then MCS has a positive and significant impact on MP. The findings indicate that improving MP requires higher OC than MCS.
Conclusion
The study's conclusion is as follows:
1) Based on test results and presented talks, MCS positively affects the performance of Perum Bulog managers at Sumsel and Babel Representative Office. As a result, the research's first hypothesis is accepted.
2) MP is unaffected by EU. Therefore, the study's first hypothesis is disproved.
3) OC cannot moderate MCS and MP's relationship. With regard to independent and dependent factors, OC is a moderate homologiser variable that exhibits no interaction. Consequently, the study's third hypothesis is disproved.
4) OC cannot mediate the EU and MP relationship. As a homologiser for moderation, OC has no interactions with independent or dependent variables. Thus, the fourth hypothesis in this study was rejected.
Based on the examination of the debate and certain findings from this investigation, the following recommendations can be made using the data from this study to achieve favorable outcomes: (a) for Perum Bulog Sumsel and Babel Representative. CS can enhance manager performance at Perum Bulog Sumsel and Babel Representative. More effectively applied management control systems will enhance management performance quality and (b) benefit future researchers. In order to increase the number of management accounting references, it is advised that future studies include additional variables in enhancing managers' performance.
References:
Adhikara, M. F., Arrozi, A., Maslichah, D. N., & Basjir, M. (2022). Organizational Performance in Environmental Uncertainty on the Indonesian Healthcare Industry: A Path Analysis. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 11(2), 365-377. https://doi.org/10.36941/ajis-2022-0058
Allen, N. J., & Meyer, J. P. (1993). Organizational commitment: Evidence of career stage effects? Journal of Business Research, 26(1), 49-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-2963(93)90042-N
Amalia, S., Rodiah, S., & Azmi, Z. (2021). Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen, Audit Operasional, Gaya Kepemimpinan, dan Disiplin Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan PT. Tri Bhakti Prima Perkasa. SNEBA: Prosiding Seminar Nasional Ekonomi, Bisnis & Akuntansi, 1, 131-142. https://ejurnal.umri.ac.id/index.php/sneba/article/ view/2746/1544
Animah, Suryantara, A. B., & Astuti, W. (2021). Pengaruh Sistem Infromasi Akuntansi Manajemen dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Terhadap Kinerja Manajer. Jurnal Akuntansi & Bisnis, 5(2), 155-171. https://doi.org/10.35308/akbis.v5i2.3998
Anthony, R. N., & Govindarahan, V. (2011). Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen. Salemba Empat.
Anwar. (2018). Efek Moderasi Dari Komitmen Organisasi Terhadap Hubungan Antara Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Anggaran Terhadap Kinerja Manajer (Survei Pada Pemerintah Daerah Kabupaten Maros). Journal for Research in Accounting, 1(1), 30-39. https://ojs.stiem-bongaya.ac.id/BJRA/article/view/29
Aprisma, R., & Sudaryati, A. (2020). Environmental Uncertainty and Firm Performance: The Moderating Role of Corporate Governance. Jurnal Akuntansi, 24(02), 187-203. http://dx.doi.org/10.24912/ja.v24i2.690
Arjalies, D. L., & Mundy, J. (2013). The use of management control systems to manage CSR strategy: A levers of control perspective, Management Accounting Research, 24(4), 284-300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2013.06.003
Arilaha, M. A., & Seber, I. S. (2019). Pengaruh Pengendalian Intern dan Good Corporate Government Terhadap Kinerja Manajer dengan Komitmen Organisasi Sebagai Variabel Moderasi (Studi Pada Perangkat Daerah Kota Ternate). Jurnal Riset Akuntansi, 7(1), 65-76. http://dx.doi.org/10.33387/jtrans.v7i1.5860
Badollahi, I., Susanto, I. R., Wahyuni, & Nurhidayah. (2022). Efektivitas Sistem Akuntansi Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan dalam Mendukung Kinerja Manajer. Jurnal Manajemen Dan Bisnis, 5(1), 644-654. https://doi.org/ 10.37531/sejaman.v5i1.1426
Bateman, T. S., & Snell, S. A. (2007). Manajemen Kepemimpinan dan Kolaborasi. Salemba Empat.
Blocher, E., Chen, K. H., & Lin, W. T. (2001). Cost management: A strategic emphasis. Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc, USA.
Chenhall, R. H. (2003). Management control systems design within its organizational context: findings from contingency-based research and directions for the future, Accounting, Organizations and Society, 28(2-3), 127-168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(01)00027-7
Cushing, B. E., & Kusasih, R. (2017). Sistem Informasi Akuntasi dan Organisasi Perusahaan. Penerbit Erlangga.
Durendez, A., Ruíz-Palomo, D., García-Pérez-de-Lema, D., & Diéguez-Soto, J. (2016). Management control systems and performance in small and medium family firms. European Journal of Family Business, 6, 10-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejfb.2016.05.001
Einhorn, S., Fietz, B., Guenther, T. W., & Guether, E. (2023). The relationship of organizational culture with management control systems and environmental management control systems. Revview Management Science, 01-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00687-0
Eriani, I. D., & Fanani, Z. (2019). Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Dan Kinerja Manajer : Peran Mediasi Sistem Akuntansi Manajemen. Jurnal Reviu Akuntansi Dan Keuangan, 9(3), 255-268. https://doi.org/10.22219/jrak.v9i3.8709
Evan, S. I. K., Gede, R. I., & Ketut, S. I. B. (2020). The role of organizational commmitment in moderating the relationship of self-efficacy on employee performace. Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic Sciences, 11(107), 12-20. https://doi.org/10.18551/rjoas.2020-11.02
Fatika, Hendra Yeka. (2022). Ombudsman RI Minta Pemerintah Segera Perbaiki Tata Kelola Cadang Beras Indonesia. Berita Obudsman Ri, March, 18. 2022. https://ombudsman.go.id/news/r/134-ribu-ton-beras-sisa-impor-2018-menumpuk-di-gudang-bulog--ombudsman-ri-minta-pemerintah-segera-perbaiki-tata-kelola-cadangan-beras-pemerintah
Ghozali, I. (2018). Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate dengan Program IBM SPSS 25. Badan Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro.
Gunawan, A. C., & Santioso, L. (2015). Pengaruh Partisipasi Anggaran Terhadap Kinerja Manajer Melalui Komitmen Organisasi Dan Motivasi Sebagai Variabel Moderating. Jurnal Akuntansi, XIX(01), 144-159. https://doi.org/10.24912/ja.v19i1.119
Guspinda, O., Bakkareng, & Putri, S. Y. A. (2021). Pengaruh Struktur Pengendalian Manajemen Terhadap Kinerja Keuangan Perusahaan Pada PT Perkebunan Nusantara VI (Persero) Kayu Aro Kerinci Jambi. Parase Jurnal, 3(1), 207-226.
Hartini, E. F., & Lestari, R. P. (2018). Pengaruh Partisipasi Penyusunan Anggaran dan Sistem Pengendalian Akuntansi Terhadap Kinerja Manajer Dengan Komitmen Organisasi Sebagai Variabel Moderating (Studi Empiris Pada PT Asuransi Umum Bumiputera Muda 1967 Kantor Pusat Jakarta). Prosiding Manajer & Kewirausahaan, 2005, 12-26.
Hayati, R. M., & Yulistia. (2023). Pengaruh Karakteristik Informasi Sistem Akuntansi Manajemen (SAM), Desentralisasi dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Terhadap Kinerja Manajer pada Kantor Polda Sumatera Barat. EPJA: Ekasakti Pareso Jurnal Akuntansi, 1(1), 23-34. https://doi.org10.31933/epja.v1i1
Heliani. (2019). Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen Terhadap Kinerja Manajer Dengan Gaya Kepemimpinan Sebagai Variabel Moderating (Penelitian pada Perusahaan BUMN yang ada di Kota Bandung). Jurnal Aktiva: Riset Akuntansi Dan Keuangan, 1(1), 38-49. https://doi.org/10.52005/aktiva.v1i1.18
Huseno, T. (2017). Organizational commitment and environmental uncertainty moderating budget participation on budgetary slack. Jurnal Aplikasi Manajemen, 15(1), 106-115. http://dx.doi.org/10.18202/jam23026332.15.1.13
Hutama, S. G., & Susilowati, E. (2021). Pengaruh Partisipasi Anggaran dan Gaya Kepemimpinan Terhadap Kinerja Manajer Melalui Komitmen Organisasi (Studi Kasus di Kantor Balai Monitor Kelas 1 Surabaya). Jurnal Manajemen Dan Akuntansi, 16(2), 427-440.
Ilias, N., Abdulatiff, N. K., & Mohamed, N. (2016). Management Control System and Performance: Accountability Attributes in Local Authorities. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 6(S4), 26-35. http: www.econjournals.com
Ilmy, N., Mus, A. R., & Ahmad, H. (2021). Pengaruh Sistem Akuntansi Manajemen Dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Terhadap Kinerja Manajer Pada Pt. Adira Dinamika Multi Finance Tbk Kantor Cabang Jayapura. Invoice : Jurnal Ilmu Akuntansi, 3(1), 129-144. https://doi.org/10.26618/inv.v3i1.4977
Junita, D., Sari, R. N., & Kurnia, P. (2018). Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen terhadap Kinerja Perusahaan dengan Strategi Bisnis Sebagai Variabel Intervening : Studi pada Perusahaan Manufaktur terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia. Jurnal Akuntansi, 6(2), 204-220.
Jusuf, R. S. (2013). Analisis Pengaruh TQM, Sistem Pengukuran Kinerja dan Reward Terhadap Kinerja Manajer. Jurnal EMBA, 1(3), 634–644. https://doi.org/10.35794/emba.1.3.2013.1870
Kartika, A. (2010). Pengaruh Komitmen Organisasi dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan dalam Hubungan Antara Partisipasi Anggaran dengan Senjangan Anggaran (Studi Empirik Pada Rumah Sakit Swasta di Kota Semarang). Journal Kajian Akuntansi, 2(1), 39-60. https://media.neliti.com/media/publications/246951-pengaruh-komitmen-organisasi-dan-ketidak-afcd7a43.pdf
Kosbiantoro, Fendy., Gunawan., Kevin & Alex S., Brian. (2018). Interaksi budaya organisasi dengan sistem pengendalian manajemen. Jurnal Manajemen: Ilmu Ekonomi dan Perpustakaan, 4 (1), 01-06. https://eprints.unmer.ac.id/id/eprint/1759/1/Jurnal%20UAS%20SPM.Fendy%20Kusbiantoro.pdf
Kwiotkowska, A., & Gębczyńska, M. (2018). The Rel between Environment Uncertainty and Enterprises Performance: A Fuzzy-Set Analysis. Multidisciplinary Aspects of Production Engineering, 1(1), 809-816. https://doi:10.2478/mape-2018-0102
Leiwakabessy, T. F. F. (2021). Komitmen Organisasi Dan Motivasi Sebagai Pemoderasi Hubungan Sistem Pengendalian Intern Pemerintah, Kompetensi Sumber Daya Manusia, Dengan Kualitas Laporan Keuangan Pemerintah Daerah. Jurnal Akuntansi : Transparansi Dan Akuntabilitas, 9(1), 29-40. https://doi.org/10.35508/jak.v9i1.3992
Mardiana, E., & Handayani, N. (2018). Pengaruh Partisipasi Anggaran Terhadap Senjangan Anggaran dengan Pemoderasi Komitmen Organisasi dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan. Jurnal Imu Dan Riset Akuntansi, 7(11), 1-20.
Manetje, O & Martins, N. (2009). The relationship between organisational culture and organisational commitment. Southern African Business Review, 13(1), 87-111. https://journals.co.za/doi/pdf/10.10520/EJC92883
Mukherji, A., & Mukherji, J. (2017). Environmental Uncertainty and Positive Performance of Small Firms: The Roles of Key Mediators. Journal of Organizational Psychology, 17(3), 24-39. https://articlegateway.com/ index.php/JOP/article/view/1673/1587
Nursam, N. (2017). Manajemen Kinerja. Kelola: Journal of Islamic Education Management, 2(2), 167-175. https://doi.org/10.24256/kelola.v2i2.438
Nursyamsir, R., Ismail, T., & Ismawati, I. (2023). Management Control System, Innovation Dan Organizational Performance. Owner : Riset Dan Jurnal Akuntansi, 7(4), 3481-3493. https://doi.org/10.33395/owner.v7i4.1839
Pratipta, H. (2015). Evaluasi Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen Pada Pusat Pendapatan Dan Pusat Biaya Untuk Meningkatkan Kinerja Manajer Penjualan. Jurnal Akuntansi Dan Sistem Teknologi Informasi, 11, 121-126. http://ejurnal.unisri. ac.id/index.php/Akuntansi/ article/view/1056
Rinaldi, A., Syazali, M., & Novalia. (2021). Statistika Inferensial untuk Ilmu Sosial dan Pendidikan (Cetakan 1). PT Penerbit IPB Press.
Sandanafu, S. P., Tjokro, C., & Ambon, P. N. (2017). Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen Terhadap Kinerja Perusahaan Dengan Teknologi Informasi Sebagai Pemoderasi (Studi Pada UMKM Sektor Kuliner Di Kota Ambon). Jurnal Maneksi, 6(2), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.31959/jm.v6i2.14
Sani, C., & Andriany, Y. (2020). Pengaruh Sistem Informasi Akuntansu Manajemen, Human Capital dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Terhadap Kinerja Manajer (Studi Kasus Pada Karyawan Bidang Manajemen Keuangan PT. Semen Padang). Jurnal Pengembangan Ilmu Akuntansi Dan Keuangan, 2(4), 269-290. https://ejurnal-unespadang.ac.id/ index.php/PJ/article/ view/234
Sari, E. N., & Saragih, F. (2020). Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen Terhadap Kinerja Keuangan Perusahaan Pada Hotel Berbintang di Kota Medan. Jurnal Riset Akuntansi Dan Bisnis, 9, 27-56. https://doi.org/10.30596/ jrab.v9i2.458
Solikhin, D. R., & Tona, A. A. (2021). Jurnal Akuntansi dan Keuangan. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 6(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.23960/jak.v26i1.276
Solimun, Fernandes, A. A. R., & Nurjannah. (2017). Metode Statistika Multivariat Pemodelan Persamaan Struktural (SEM) Pendekatan WarpPLS. UB Press.
Sripeni, R. (2014). Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen Terhadap Kinerja Manajer Pada BPR Eka Dharma Binaraharja Magetan. 14(1), 9-25.
Sugiyono, D. (2019). Metode Penelitian Bisnis. Alfabeta.
Suhardi, M. (2020). Pengaruh Team Work Dan Organization Learning Terhadap Komitmen Organisasi Kepala Sekolah Smp Negeri Di Kota Mataram. Jurnal Visionary : Penelitian Dan Pengembangan Dibidang Administrasi Pendidikan, 4(2), 116-123. https://doi.org/ 10.33394/vis.v4i2.3004
Sujarweni, W. (2019). SPSS Untuk Penelitian. Pustaka Baru Press.
Sumarsan, T. (2013). Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen: Konsep, Aplikasi, dan Pengukuran Kinerja. Edisi 2. (2nd ed.). PT Indeks.
Suparmun, H. (2015). Pengaruh Partisipasi Anggaran terhadap Kinerja Manajer : Komitmen Organisasi dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Sebagai Moderasi. Jurnal Ekonomi Bisnis Manajemen Prima, 17(1), 77-84. https://doi.org/10.34012/ jebim.v2i1.1179
Sutanto, E. M., & Ratna, A. (2015). Pengaruh Komitmen Organisasional Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan Berdasarkan Karakteristik Individual. Bisma Jurnal Bisnis Dan Manajemen, 9(1), 56-70. https://jurnal.unej.ac.id/index.php/BISMA/article/view/5902
Tendean, A. B., Saerang, D. P. E., & Runtu, T. (2018). Pengaruh Struktur Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen, Proses Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen Dan Sistem Penghargaan Terhadap Kinerja Manajer (Studi Pada RSUD Sulawesi Utara). Going Concern : Jurnal Riset Akuntansi, 13(04), 597-610. https://doi.org/10.32400/gc.13.03.20776.2018
Umar, H. (2003). Metode Riset Bisnis Panduan Mahasiswa untuk Melaksanakan Riset Dilengkapi Contoh Proposal dan Hasil Riset Bidang Manajemen dan 75 Akuntansi. PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Wahyuni, S. W., & Lestari, R. (2019). Pengaruh Penerapan Sistem Akuntansi Manajemen Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Kinerja Manajer Bank. Jurnal Analisa Akuntansi Dan Perpajakan, 2(2), 703-707. https://doi.org/10.29313/ v6i2.24123
Wati, N. P., & Damayanti, I. G. (2017). Pengaruh Partisipasi Penganggaran, AsimetriInfomasi, Ketidakpastian Lingkungan dan Budget Emphasis Pada Senjangan Aggaran. E-Jurnal Akuntansi Universitas Udayana, 21(3), 2311-2337. https://doi.org/10.24843/EJA.2017.v21.i03.p22
Wijaya, R. S. (2022). Pengaruh Sistem Akuntansi Manajemen, Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen, dan Ketidakpastian Lingkungan Terhadap Kinerja Manajer (Studi Penelitian pada PT Semen Padang, Lubuk Kilangan, Padang). Jurnal Penelitian Dan Kalian Ilmiah Menara Ilmu, XVI(01), 70-78. https://doi.org/10.31869/mi.v16i.3418
Wiratno, A., Ningsih, W., & Putri, N. K. (2016). Partisipasi Anggaran Terhadap Kinerja Manajer. Jurnal Akuntansi, XX(01), 150-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.24912/ja.v20i1.81
Download Count : 122
Visit Count : 258
Keywords
Managers’ Performance; Environment Uncertainty; Management Control System; Organizational Commitment
How to cite this article:
Zakiah, N. S., Susanto, H., Mukhtaruddin, & Gozali, E. O. D. (2024). Management Control System, Environment Uncertainity and Manager’s Performance: Organization Commitment as a Moderating Variable. European Journal of Studies in Management and Business, 30, 57-75. https://doi.org/10.32038/mbrq.2024.30.04
Acknowledgments
I would like to express my gratitude to Professor Mohamad Adam as Dean Faculty of Economic Universitas Sriwijaya dan Arista Hakiki, M. Acc as Chairman of Accounting Department Faculty of Economic Universitas Sriwijaya have supported our team to publish this article.
Funding
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interests
No, there are no conflicting interests.
Open Access
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. You may view a copy of Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License here: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/







